- Mariposa Computer Science Magnet School
- What is PBIS?
-
What is PBIS?
PBIS (Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports) is an organized, data-driven system of interventions, strategies, and supports that positively impact school-wide and individual behavior planning.
Using the most current best practices, strategic teams are trained to positively impact behavior at three key behavioral tiers: Universal or primary (whole school); Secondary (individual child or group of at-risk children); and Tertiary or Intensive (children with complex needs and behaviors that severely impact the child, school and/or community functioning).
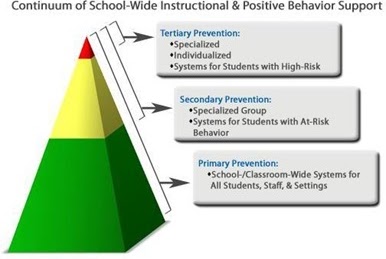 Why is it so important to focus on teaching positive school behaviors?
Why is it so important to focus on teaching positive school behaviors?Frequently, the question is asked, “Why should I have to teach kids to be good? They already know what they are supposed to do. Why can I not just expect good behavior?” In the infamous words of a TV personality, “How is it working out for you?”
In the past, school-wide discipline has focused mainly on reacting to specific student misbehavior by implementing punishment-based strategies including reprimands, loss of privileges, offices referrals, suspensions, and expulsions. Research has shown that the implementation of punishment, especially when used inconsistently and in the absence of other positive strategies, is ineffective. Introducing, modeling, and reinforcing positive social behavior is an important step of a student’s educational experience. Teaching behavioral expectations and rewarding students for following them is a much more positive approach than waiting for misbehavior to occur before responding. The purpose of school-wide PBIS is to establish a climate in which appropriate behavior is the norm.
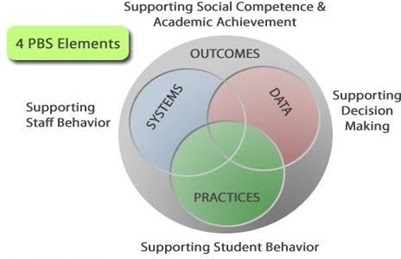
What is a systems approach in school-wide PBIS?An organization is a group of individuals who behave together to achieve a common goal. Systems are needed to support the collective use of best practices by individuals within the organization. The school-wide PBIS process emphasizes the creation of systems that support the adoption and durable implementation of evidence-based practices and procedures, and fit within on-going school reform efforts. An interactive approach that includes opportunities to correct and improve four key elements is used in school-wide PBS focusing on: 1) Outcomes, 2) Data, 3) Practices, and 4) Systems. The diagram below illustrates how these key elements work together to build a sustainable system:
-
Outcomes: academic and behavior targets that are endorsed and emphasized by students, families, and educators. (What is important to each particular learning community?)
-
Practices: interventions and strategies that are evidence based. (How will you reach the goals?)
-
Data: information that is used to identify status, need for change, and effects of interventions. (What data will you use to support your success or barriers?)
-
Systems: supports that are needed to enable the accurate and durable implementation of the practices of PBIS. (What durable systems can be implemented that will sustain this over the long haul?)
What does this mean for staff?-
All staff need to recognize and acknowledge children who are following the school-wide expectations.
-
All staff need to be ready to give out Monarch Bucks to students in the classroom and throughout the building.
-
All staff need to know the Behavior Flow Chart and be consistent with their responses.
-
All staff need to complete an Office Discipline Referral Form if a child’s response to a problem behavior indicates the need.
-
Teaching staff need to post the School-wide Expectations in their class and other areas that children often use.
-
Teaching staff need to include the “Cool Tools” in their lesson plans as indicated on the Expectation Schedule and as needed (for whole group or individuals).
-
All staff need to CELEBRATE successes as much as possible!
-


